RADIATION NETWORKS:
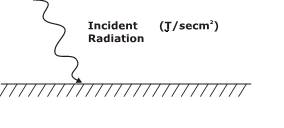
IRRADIATION (G)
Irradiation (G) is defined as the total thermal radiation incident upon a surface per unit time per unit area (in W/m2)
RADIOSITY (J):
The total thermal radiation leaving a surface per unit time & per unit area is called radiosity of the surface.

J = Emitted Energy + Reflected Part of Incident energy,
The net radiation heat exchange between the surface & all of its surroundings is given by,
The equivalent radiation circuit is,

Radiation heat exchange between two finite surfaces:
,The equivalent radiation circuit is
This space resistance shall exist in the space between two surfaces exchanging heat by radiation.
Complete radiation network between two surfaces exchanging heat by radiation:
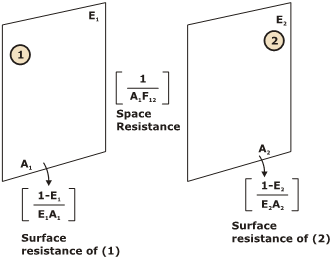
Therefore,
APPLICATIONS OF RADIATIONS NETWORKS:
(i) Radiation Exchange Between two Infinitely Large Plane Surfaces:
(ii) TWO INFINITELY LONG CYLINDERS:
Therefore,
RADIATION SHIELDS:
F12 = 1, F21 = 1
Since surfaces are very large
A1 = A2 = A3 = 1 and F13 = 1, F32 = 1
Therefore,
No comments:
Post a Comment
Knowing brings controversy