Rankine Cycle:
The Rankine cycle is the fundamental operating cycle of all power plants where an operating fluid is continuously evaporated and condensed.
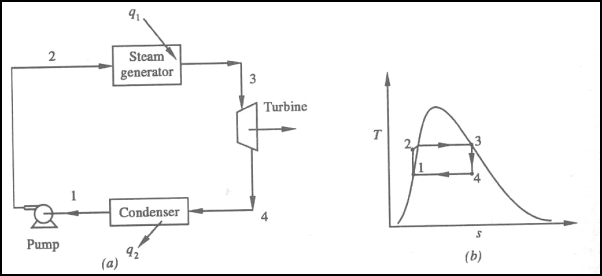
2-3 Isobaric Heat Transfer:
High-pressure liquid enters the boiler from the feed pump (1-2) and is heated to the saturation temperature (2). Further addition of energy causes evaporation of the liquid until it is fully converted to saturated steam (3).3-4 Isentropic Expansion:
The vapour is expanded in the turbine, thus producing work which may be converted to electricity. In practice, the expansion is limited by the temperature of the cooling medium and by the erosion of the turbine blades by liquid entrainment in the vapour stream as the process moves further into the two-phase region. Exit vapour qualities should be greater than 90%.4-1 Isobaric Heat Rejection:
The vapour-liquid mixture leaving the turbine (3-4) is condensed at low pressure, usually in a surface condenser using cooling water. In well designed and maintained condensers, the pressure of the vapour is well below atmospheric pressure, approaching the saturation pressure of the operating fluid at the cooling water temperature.1-2 Isentropic Compression:
The pressure of the condensate is raised in the feed pump. Because of the low specific volume of liquids, the pump work is relatively small and often neglected in thermodynamic calculations.Work done on pump, per kg of water: WP= h2 – h1
Energy added in steam generator: q1= h3 – h2
Work delivered by turbine: WT= h3 – h4
Energy rejected in the condenser, q2 =h4 – h1
- The thermal efficiency of the Rankine cycle is given by:
Reheating of Steam:
In the reheat cycle, the expansion of steam from the initial state 1 to the condenser pressure is carried out in two or more steps depending upon the number of reheats used.
Cycle efficiency: improves with reheat, however the cycle efficiency in a single reheat plant is influenced by pressure at which steam is reheated. The efficiency increases as the reheat pressure is lowered and reaches a peak at a pressure ratio between 0.20 and 0.25.

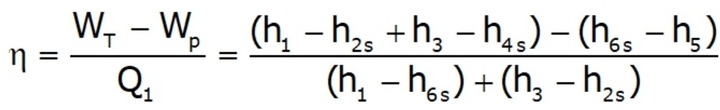
Reheating steam also increase the net work output of turbine.
Key Points:
- Internal irreversibility of Rankine cycle (Real cycle) is caused by fluid frictions throttling and mixing.
- Externally, irreversibility of the Rankine cycle is caused due to the temperature difference between the combustion gases and the working fluid on the same side and the temperature difference between the condensing working fluid and the condenser cooling water on the sink side.
Advantages of Re‑heating:
- Due to reheating, network done increases.
- Heat supply increases.
- Thermal efficiency mat increase or decrease depending upon the mean temperature of heat addition.
- Due to reheating, the turbine exit dryness fraction increases so moisture decreases ‑ so blade erosion becomes minimum ‑ so life of the turbine will be increased.
Regeneration:
(i). The mean temperature of heat addition (and so efficiency) can also be increased by reducing the amount of heat added at low temperatures in the economizer section of steam generator.
(ii). In the regeneration process energy is exchanged internally between the expanding fluid in the turbine and the compressed fluid before heat addition.
(iii). Ideal regenerative cycle done not affect work output from turbine, it is more efficient with high steam rate.

Efficiency of Steam Power Plant: Overall efficiency of the steam per plant is given by
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
- Reheating of steam improved the thermal efficiency of the plant, net work output of turbine, reduction in blade erosion (or quality of steam improve).
- By regeneration thermal efficiency of the plant can be increased but it does not affect work output from turbine.
Combined Cycle Power Generation:
It is an assembly of heat engines that works with the same source of heat. The principle of combined cycle power generation is that the exhaust of one heat engine is used as the used as the source of heat for another heat engine. This process increases the overall efficiency of a heat engine.
![]()
Advantages of Regeneration cycle:
- Heat supplied to boiler becomes reduced
- Thermal efficiency is increased since the average temperature of heat addition to the cycle is increased.
- Due to bleeding in the turbine, erosion of turbine due to moisture is reduced.
Characteristics of Ideal Working Fluid
- The fluid should have high critical temperature and the saturation pressure at the temperature of heat rejection should be above the atmospheric pressure.
- Specific heat of liquid should be small.
- The saturated vapour line of T-s diagram, very close to the turbine expansion process.
- The freezing point of the fluid should be below the room temperature.
- The fluid should be chemically stable, non-toxic, non-corrosive, not excessively viscous and low in cost.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Knowing brings controversy