Refrigeration Cycle:
Refrigeration is the process in which heat is removed from a body or enclosed space and its temperature is maintained at the temperature below the surrounding temperature.
The working substance used in refrigeration cycle to produce require effect i.e. cooling is known as refrigerant.
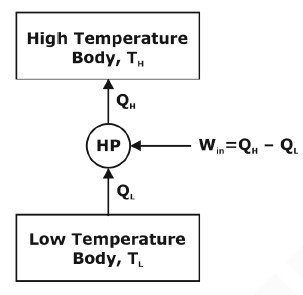
Heat Pump: Heat pump is a device which is used to maintain a space at higher temperature than that of surroundings, for which external work has to be supplied.
Coefficient of Performance:
![]()
Here, the desired effect is to maintain the body at a temperature higher than that of surrounding.
Thus,
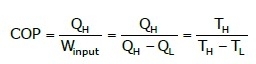
where:
TH = High temperature body
TL = Low temperature body
Refrigerator: It is a device which is used to maintain a body at a temperature lower than the temperature of the surrounding.
![]()

Where, TH = Constant temperture at which heat is to be rejected
TL = Constant temperture from where heat is to be extracted
(COP)HP = (COP)R + 1

where, QL= heat at lower temperature,
QH = heat at higher temperature
Unit of Refrigeration: It has standard unit of TR (Ton or Refrigeration). 1 TR (one ton of refrigeration) means capacity to freeze one ton of water from and at 0oC in 24 h.

Key Points
- A refrigerator is a device operating in a cycle, maintains a body at a temperature lower than that of the surroundings.
- There is performance parameter in a refrigerator cycle, called the coefficient of performance.
- Heat pump is a device which operating in a cycle, maintains a body at a temperature higher than the temperature of the surroundings.
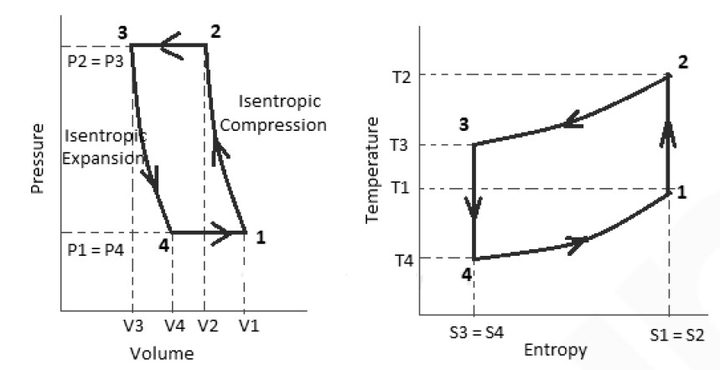
Reversed Carnot Cycle:
When the processes of Carnot cycle is reversed, then it is called reversed Carnot cycle.


![]()

Where T2 and T1 are the temperature at section 2 and 1 respectively and S1, S2, S3 and S4 are the entropy at 1, 2, 3 and 4 respectively.
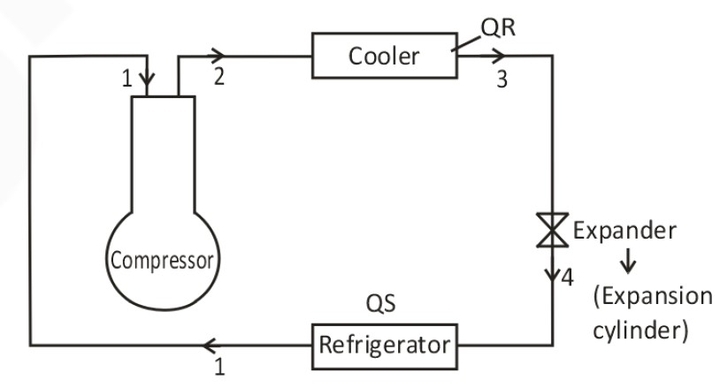
Vapour Compression Refrigeration System:
In this system, refrigerant extract the heat from one place and release at the other thus maintaining the place at lower temperature.
When refrigerent passes through the evaporator, it extracted the heat from the chamber and converts in to vapour and produces refrigerating effect. This process is known as evaporation.


1 → 2 → Isentropic compression process
2 → 3 → condensation process (constant pressure Heat Rejection)
3 → 4 → Isenthalpic Expansion process
4 → 1 → evaporation process (constant pressure Heat Addition)

Where h1 = Enthalpy at the inlet of compressor
h2 = Enthalpy at the exit of compressor or inlet of condenser
h4 =Enthalpy at the exit of condenser or inlet of throttle valve

![]()
Key Points
- COP of refrigerator working between two fixed temperature TL and TH (TH > TL) will have fixed COP.
- A reversible heat engine can work like a refrigerator or a heat pump.
- Vapour compression refrigeration cycle
- Entropy:

h2 = h2'+Cp (T2' –T2) - For isentropic process:
S2 = S1
Air Refrigeration System:
In air refrigeration, Bell Coleman cycle is used which works on reversed Brayton cycle while Brayton cycle is used for gas turbine.
COP of reversed Brayton cycle:
Let pressure ratio: rp, then:
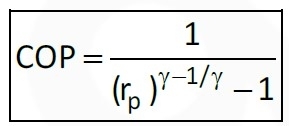
Where, γ = index, rp = pressure ratio
Compressor:
A compressor is used in refrigerator to increase the pressure of gas.
IN VCRS system, we generally prefer reciprocating compressor.
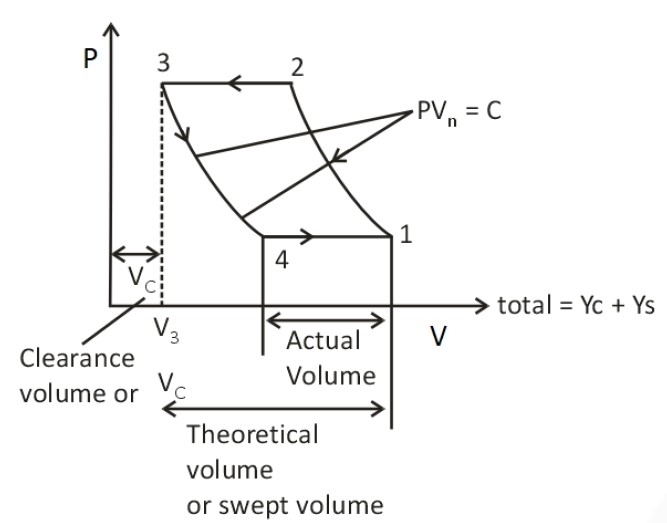
Clearance ratio:

Swept volume:
![]()
Volumetric efficiency is given by:
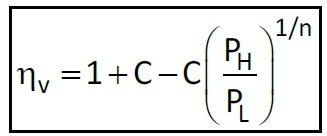
where, D = diameter of compressor
L = stroke length
n = N for 2 stroke
n = N/2 for 4 stroke
N = rotational speed
ηv = volumetric efficiency
k = number of cylinders
Vc = clearance volume
C = clearance ratio
Vapour Absorption Refrigeration System (VARS):
This system utilizes low grade energy or waste energy to produce refrigeration effect.
In vapour absorption system compressor is replaced by a unit comprising an absorber, a pump and a generator.

COP of an Ideal Vapour Absorption System:
Schematic diagram of energy transfer in vapour absorption system is shown below

Qg = heat supply to refrigerator in generator
Qe = heat is absorbed by refrigerator in evaporator
Qc = heat is rejected to condenser or atmosphere
Coefficient of Performance:
Qg + Qe = Qc
For reversible cycle net entropy change is zero.



COP of Carnot refrigerator ![]()
Efficiency of Carnot engine 
Here, Tg = generator temperature
Tc = To = absorber temperature (Generally surrounding temperature)
Te = evaporator temperature.
Refrigerant:
Refrigerant is the fluid which flows through the various components of refrigeration system and absorbs heat by vaporization at evaporator and rejects it through condensation at condenser and so produces refrigerating effect.
Designation of Refrigerant:
In International Standards, Refrigerants are designated as R followed by some numeric values.
For a hydrocarbon Chemical formula: Cr Hs Ft Cly
If S+t+y=2r+2, designation of refrigerant is R(r-1)(S+1)t
It S+t+y=2r, designation of refrigerant is R1(r-1)(S+1)t
For an Inorganic Refrigerant:
Designation is R(700 + molecular weight)
e.g. ![]()
Desirable Properties of a Good Refrigerant
- Low boiling point
- Low freezing point
- High latent heat of vaporization
- High thermal conductivity
- Low viscosity
- Low specific volume in vapour state
Uses and Properties of Some Refrigerant
- In absorption refrigeration system, we use NH3 – H2O or water lithium bromide or water lithium chloride. In NH3 – H2O system NH3 is refrigerant while H2O is transport medium. In water lithium bromide or water lithium chloride water if refrigerant.
- In ice plant, primary refrigerant is NH3 or Freon while secondary refrigerant is prime solution.
- Freezing temperature of Freon-12 is – 157.8oC, so it is not used for producing temperature below the freezing temperature.
- In dehydrator, silica get (molecular sieve SiO2 + K2O + NO2 + Al2O3) is used with calcium chloride. (Not use sodium chloride).
- Hermetically sealed reciprocating compressor is commonly used in room air conditioner.
- For passenger aircraft air is used as refrigerant.
- Refrigerant CO2 has lowest specific volume.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Knowing brings controversy