thermal stresses are due to the change in temperature of the component and the component is mechanically restrained to expand or contract.
Conditions for existence of Thermal Stress:
- There should be a temperature change in the component.
- The thermal expansion or contraction should be restricted either completely or partially.
When the temperature of an object changes, its dimensions are changed which results in strain.
If α is the coefficient of thermal expansion (or contraction), the uniform thermal strain (ϵt) is given by:
![]()
Where ΔT is the change in temperature.
So, change in length is given by,
![]()
Where L is the initial length.
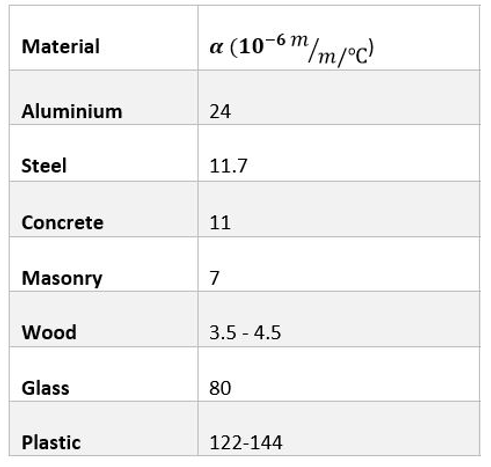
coefficient of thermal expansion - The coefficient (α) is a property of the material and has a unit reciprocal of temperature change.
List of materials and their coefficient of thermal expansion.
Thermal stress under different stress condition
Case (a): When bar is free to expand:
Consider a bar of length L subjected to uniform temperature increase T, the bar being free to expand. Then the increase in the length of bar will be:
![]()
since the bar is free to expand, there will be no thermal stress in the bar.
Case (b): When bar is constrained:
consider a bar of length L, fixed at both ends between rigid supports.
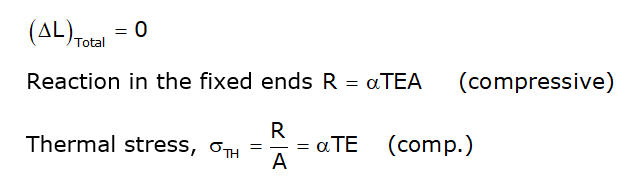
This stress will be compressive when the change in temperature (T) is positive (i.e. increase) and tensile. When the change in temperature is negative (i.e. decrease).
Case (c): When Supports yield:
If the support yields by an amount λ. In this case, the total amount of expansion checked will be (ΔT - λ) .
Thus,
![]()
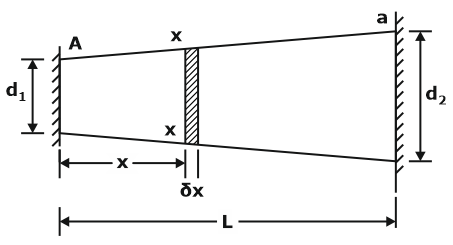
TEMPERATURE STRESSES IN BARS OF TAPERING SECTION
Consider a bar of uniformly tapering section, shown in Figure, rigidly fixed between two end supports. When the temperature is raised by ΔT,
Tapering bar with increasing cross-section
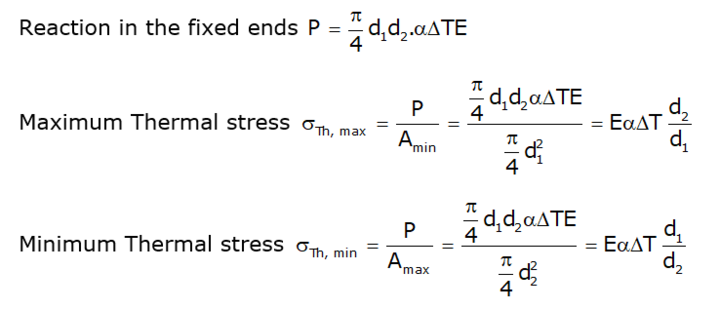
THERMAL STRESSES IN COMPOUNDS AND COMPOSITE BARS
Thermal stresses in compound bars (BARS in series):
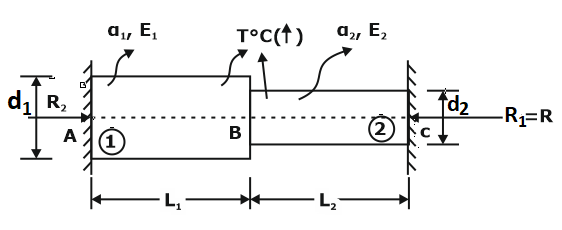
Bars in series

TEMPERATURE STRESSES IN COMPOSITE BAR
When a composite bar, consisting of two materials having different coefficients of thermal expansion, is subjected to temperature change, opposite kinds of stresses (i.e. tensile and compressive) will be set up in the two materials.
Consider a composite bar of steel (S) and copper (C), subjected to increase in temperature.
https://gs-post-images.grdp.co/2020/8/11-img1596912533756-36.png-rs-high-webp.png
The free expansion of copper due to temperature rise will be less in steel since for copper is more than of steel. In order to have common expansion , tensile stress will be developed in steel and compressive stress in copper.
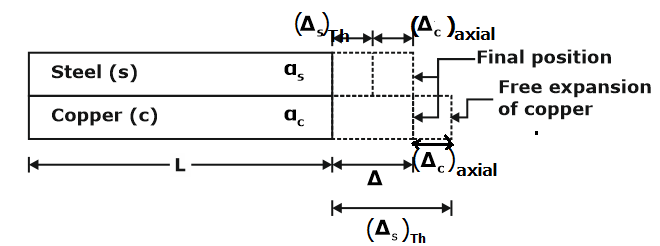
Bars connected in parallel
Tensile force in steel = compressive force in copper
![]()
From compatibility equation
Final extension of copper = Final extension of steel
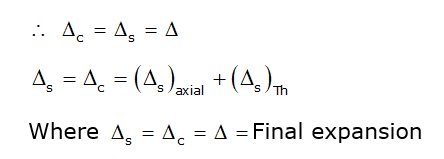
(Δs)Th = Free expansion of steel, due to temperature rise
(Δc)Th =Free expansion of copper, due to temperature rise
(Δs)axial = Expansion of steel due to temperature stress (tensile)
(Δc)axial = Compression of copper due to Temperature stress (comp.)
Results,

Substituting the value of P
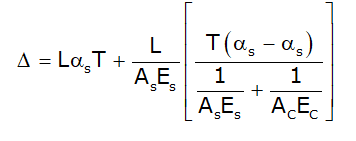
Exomechanicals: Thermal Stress >>>>> Download Now
ReplyDelete>>>>> Download Full
Exomechanicals: Thermal Stress >>>>> Download LINK
>>>>> Download Now
Exomechanicals: Thermal Stress >>>>> Download Full
>>>>> Download LINK